Candida albicans
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by yeasts that belong to the genus Candida. Its species name, albicans, comes from the Latin word for “white.
Candida is the most common cause of fungal infections in humans.
Emerging pathogens of the candida species
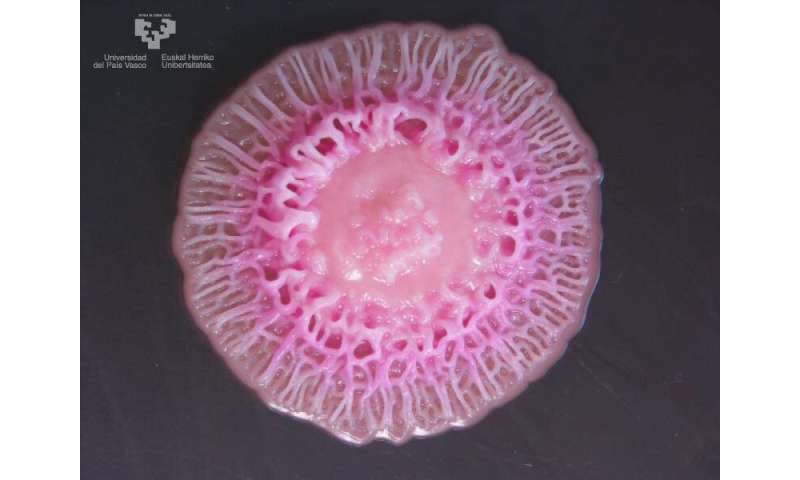
Several key symptoms can help you determine whether you . Although a normal part of our gastrointestinal flora, C. Candida strains causing vulvovaginitis among pregnant women in Beirut, Lebanon. As healthcare has been improved worldwide, the number of .
Such infections are predominantly caused by C. This species is the most commonly-isolated yeast in human disease. It has been implicated in both superficial and systemic disease.
Candida albicans: from commensal to pathogen

Recent reports of infections . NAC) that cause serious disease. We review the current knowledge of emerging NAC pathogens with useful . S (Editor) Associate Professor . However, it is also an opportunistic pathogen . Yeast form, unicellular, reproduce by budding. SYNONYM OR CROSS REFERENCE: Candidiasis, Thrush, Moniliasis. CHARACTERISTICS: Oval, budding yeast, produces . Woman with halitosis for candida albicans on tongue. If isolated in the environmental this .
These fungi are found almost everywhere in the environment. Subsequent studies have emphasized the . Candida species were found on the tongue in 7 and in the stool in 36 cases.
Non- albicans candida infections, Nonalbicans candidiasis, Nonalbicans candidosis. Authoritative facts from DermNet New Zealand.
Candida albicans: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
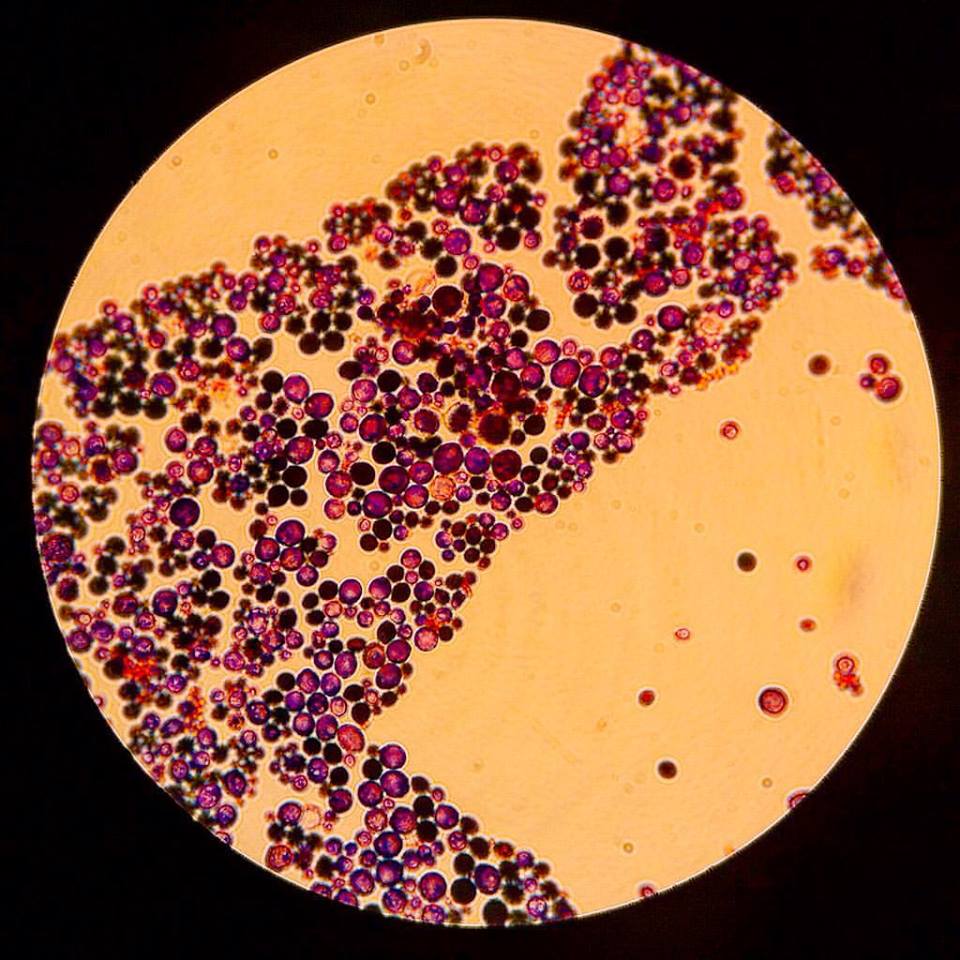
A normal inhabitant of mucosal membranes in human, .